Migrating from Oracle EBS to Fusion Cloud
Companies globally are contemplating moving from on-premise software from the legacy side to the cloud. Cost of ownership is a major concern experienced by users of on-premise software like E-Business Suite. This journey of migrating to the cloud needs harmonizing of processes. However, working towards an ideal migration plan and a comfortable pace is key in such decisions. This transition requires change management, alignment of teams, and consultation on best practices.
Challenges with EBS Suite
With on-premise, hardware refreshes & software updates are a necessity. But moving to the latest release is often daunting, costly & requires downtime for the system, a reason why it is largely deferred by businesses. But it is essential to perform these updates to avoid the risk of vulnerability. Fixing issues & bugs takes a longer duration with delayed updates. The same is the case with security patches where regular costly updates are to be performed to ensure security.
The TCO with on-Premise is higher owing to the initial hardware and software investment and the subsequent costs involved with the refreshes and updates.
A typical concern is the building up of out-of-date and disorganized information in an EBS environment. This may lead to lags, inaccuracies & inefficiencies. Transient data and obsolete transactional data must be repeatedly purged from the EBS platform so that only relevant data is worked upon for business insights.
For EBS 12.1 users, the support ends by December 2021. During this period, the support is limited to Severity 1 Service Requests (SRs), functional issues, and security updates (critical patch update program). Such situations demand organizations to approach upgrades or migration at the earliest.
Why migrate to Fusion Cloud?
Lower Costs: The TCO is lowered by almost 38% vis-a-vis on-premises deployments. It manages and reduces capital expenditures and transforms them into predictable operating expenditures by way of efficient data center maintenance, eliminating server hardware, and taking advantage of cloud flexibility wherever possible.
The “pay-as-you-go” usage model just adds to the benefits. Also, the provision to bring existing Oracle licenses to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and leverage existing investments, including monitoring, operational runbooks, skills, and workflow, add significantly to the value.
Better Performance: Fusion Cloud results in 30% increased performance and 2-10 times faster reporting. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure delivers higher-performance computing, storage, networking, and managed database instances, giving users a high-performance experience. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is the only platform where Oracle Database can be run with Oracle RAC or Oracle Database Exadata Cloud Service. Other cloud systems have lesser robust configurations.
Easier to manage: With Oracle’s specific tooling and automation to streamline deployment, migration, upgrading, and maintaining implementation, it saves time and reduces risk. The implementation timeline is in weeks, rather than months. A typical deployment can be done within 12-14 weeks.
Easier to use: The cloud-based access provides seamless navigable dashboards for efficient troubleshooting. When compared to EBS, in fusion there is no need to run multiple queries for the creation of ad-hoc reports for real-time data. Enabled with Guided Business Processes, which are organized sets of tasks, there is help in getting work done more efficiently.
Reporting Capabilities of Oracle Fusion Cloud
Oracle Transactional Business Intelligence (OTBI): Provides real-time transactional analytics, reports, charts/graphs, and flexible outputs embedded within Cloud Applications. This tool is recommended for business users for ad-hoc analysis and daily reporting.
BI Publisher: Recommended for creating customer-facing documents and complex reporting.
Oracle Financial Reporting Studio (FR Studio): A powerful tool for accessing, designing, and presenting financial reports and analytical data. This tool is recommended for Financial Analysts who must create financial reports for regulatory compliance.
Smart View: An Excel-based analysis tool and is recommended for usage by Financial Analysts for slicing/dicing analysis
- The data model of Fusion is a combination of Oracle EBS, Siebel, and PeopleSoft.
- Oracle Fusion Applications uses trees, a hierarchy model that offers flexible hierarchies for crossing lines of business processes.
- The tree structure is in the data model and is used directly in the Java business logic and exposed through Oracle Business Intelligence.
- A unified metadata dictionary, and a metadata store, accessible to all the tools, provide consistency for all the components in the technology stack and enable you to preserve changes across upgrades.
Fusion Architecture
Oracle fusion applications are built on Oracle fusion middleware technology. This is robust and offers numerous add-ons for fusion applications.
Apart from application servers, it has identity management, SOA, BI, ODI, BPM & WebLogic communication, which enables seamless connection with the database through the WebLogic server.
One of the primary highlights of Fusion is that it uses a service-oriented architecture (SOA). SOA uses orchestration technology to assemble various services to provide comprehensive functionality.
This allows a newer, much smoother approach in contrast to the forms and database-centric approach of the Oracle application architecture in EBS.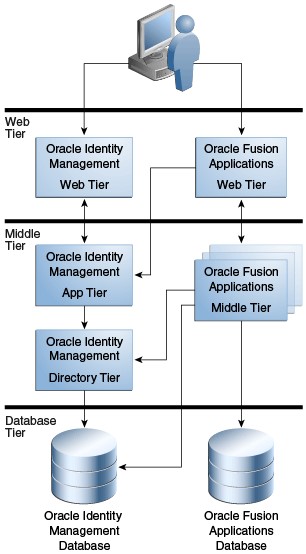
ennVee Approach in, migration from EBS to Fusion Cloud
Like any conventional migration process, the phases are planning, preparation, pre-migration, downtime, and post-migration.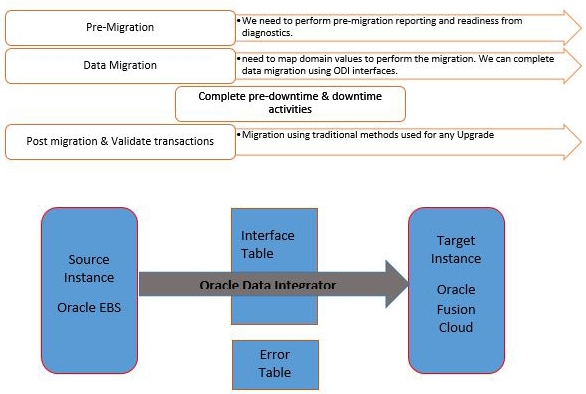
These needs performing pre-migration reporting and readiness from diagnostics. A readiness report, both in summary and in detail is done to check the overall readiness status. If the report is completed with one or more errors, then a search for ‘failure’ would be initiated and the corrections instilled before attempting to upgrade. These readiness checks can be re-run as many times as necessary before an upgrade.
Few Things to consider before Migration
- Presentation of a summary picture by product and feature as to what cannot be migrated
- Customer review of the potential areas and decision-making before the start of the migration
- Checking all the detailed exception reports for all products. The EBS to Fusion Migration offering in the Fusion setup manager will be used for the same
Finally, the domain values are mapped to perform the data migration and are completed using ODI interfaces.
- Set-up data
- Transactional data
- Descriptive Flex Fields like schemas related to controlled customizations
- Extension using API hooks
- OA Personalization Framework customizations in e-Business Suite will not be migrated
- Oracle Forms personalization and customizations
- Oracle Workflows customizations
- Report customization
- Non-controlled Schema Customization
- On-premise, hosted by the enterprise
- Public cloud-hosted over the Internet by Oracle, software as a service (SaaS)
- Private Cloud, internally behind a firewall hosted as a SaaS
- Hybrid, an implementation of both on-premise and cloud
What can the right Implementation Partner offer in Migration decisions?
- Transfers mission-critical systems to Cloud with minimal downtime and risk
- Helps in accelerating the migration journey through proven, mature, and rigorous ITIL-driven operational processes
- Helps define the business case objectives and goals
- Further assists in inventorying Oracle EBS applications and planning migration strategies
- Designs migrate and validate each application by following a meticulous and iterative path to the new operating model
- Implementing solutions with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to spot known and unknown threats
- Handles day-to-day post-migration administration, while providing full visibility into the environment, reducing time spent by the internal team on IT management